Multistage Centrifugal Pumps
Text №1
Vertical Сentrifugal Pumps1
Vertical centrifugal pumps1 are also referred to as cantilever pumps2. They utilize a unique shaft and bearing support3 configuration that allows the volute to hang in the sump4 while the bearings are outside of the sump. This style of pump uses no stuffing box5 to seal the shaft but instead utilizes a "throttle bushing"6. A common application for this style of pump is in a parts washer7.
Froth pumps8
In the mineral processing industry, or in the extraction of oil sand9, froth is generated to separate the rich minerals or bitumen from the sand and clays. Froth contains air that tends to block conventional pumps and cause loss of prime10. Over history, industry has developed different ways to deal with this problem. One approach consists of using vertical pumps with a tank. Another approach is to build special pumps with an impeller capable of breaking the air bubbles. In the pulp and paper industry holes are drilled in the impeller11. Air escapes to the back of the impeller and a special expeller12 discharges the air back to the suction tank13. The impeller may also feature special small vanes between the primary vanes called split vanes or secondary vanes. Some pumps may feature a large eye, an inducer14 or recirculation of pressurized froth from the pump discharge15 back to the suction to break the bubbles.
1. vertical centrifugal pump– вертикальный центробежный насос
2. cantilever pump– консольный насос
3. bearing support –подшипниковая опора\
4. sump –грязеотстойник; грязевик; резервуар
5. stuffing box –гидравлический сальник
6. throttle bushing –дроссельная втулка, гильза
7. parts washer –моечная машина; моечная установка
8. froth pump –пенный насос
9. oil sand –нефтеносный песок, битуминозный песок
10. prime –захлебывание
11. impeller –лопастное колесо, крыльчатка
12. expeller –шнековый пресс
13. suction tank– приёмный резервуар
14. inducer –устройство для подачи (жидкости) под давлением
15. pump discharge –выкид насоса; нагнетательное отверстие насоса
Text №2
Multistage Centrifugal Pumps
A centrifugal pump containing two or more impellers is called a multistage centrifugal pump1. The impellers2 may be mounted on the same shaft or on different shafts.
For higher pressures at the outlet impellers can be connected in series3.
For higher flow output impellers can be connected in parallel.
All energy transferred to the fluid is derived from the mechanical energy driving the impeller.
The energy usage in a pumping installation is determined by the flow required, the height lifted and the length and friction characteristics of the pipeline. The power required to drive a pump ( 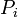 ), is defined simply using SI units by:
), is defined simply using SI units by:
Single-stage radial-flow centrifugal pump
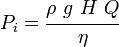
where:
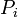 is the input power required (W)
is the input power required (W)
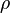 is the fluid density (kg/m3)
is the fluid density (kg/m3)
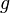 is the standard acceleration of gravity (9.80665 m/s2)
is the standard acceleration of gravity (9.80665 m/s2)
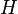 is the energy Head added to the flow (m)
is the energy Head added to the flow (m)
 is the flow rate (m3/s)
is the flow rate (m3/s)
 is the efficiency of the pump plant as a decimal4
is the efficiency of the pump plant as a decimal4
The head5added by the pump ( 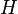 ) is a sum of the static lift, the head loss due to friction and any losses due to valves or pipe bends all expressed in meters of fluid. Power is more commonly expressed as kilowatts (103 W, kW) or horsepower (kW = hp*0.746). The value for the pump efficiency,
) is a sum of the static lift, the head loss due to friction and any losses due to valves or pipe bends all expressed in meters of fluid. Power is more commonly expressed as kilowatts (103 W, kW) or horsepower (kW = hp*0.746). The value for the pump efficiency,  , may be stated for the pump itself or as a combined efficiency of the pump and motor system.
, may be stated for the pump itself or as a combined efficiency of the pump and motor system.
The energy usage is determined by multiplying6 the power requirement by the length of time the pump is operating.
1. multistage centrifugal pump –многоступенчатый центробежный насос
2. impeller –лопастное колесо, крыльчатка
3. in series –последовательно
4. decimal –десятичная дробь
5. head –напор
6. multiplying– умножение
Text №3