Features of restoration of the atypical cavities and pulpless teeth
Pulpless tooth, in contrast to intact, is very fragile and often of another color, which is caused by loss of basic tooth structure - dentine. Enamel without dentine is also very fragile and often breaks as a result of chewing loading. That is why, restoration of teeth after endodontic treatment should be carried out with taking into consideration structural and functional peculiarities of hard tissue of pulpless tooth group belonging and performed function. Materials for filling atypical cavities are composites and compomers, glass ionomers increased strength. For strengthening of remaining tooth walls with the help of monolith, occupying the whole chewing surface, as a support in a root canal are used pins.
Parapulpar pins -a special beam structures of metal alloys (stainless steel, alloys of gold, titanium, or a combination of metal-coated), intended for the reinforcement and retention of filling material and installed in the hard tissues of the tooth out of pulp cavity.
There are three main types of systems of pins:
1.Cemented - a kind of pins that stick with cement in a prepared recess in the dentin. Its surface is smooth. It is the only pin that you can try in a prepared recess, and then remove it.
2.Friction locked - a kind of pins with a diameter greater than the diameter of the deepening of the dentin. It is entered under pressure into the groove hammer by friction.
3. Screwed - a kind of pins with a diameter as the diameter of the deepening of the dentin, but it is introduced by thread, and not on the line. This type of pin retention gives the seal to five times more than cemented pin.
Pins at construction classified by the following principles:
1) by elasticity: elastic, not elastic;
2) by material: ceramic, metal (steel, silver, nickel-titanium), fiber (synthetic fiber);
3) for fixation: passive (cemented), active (screwed);
4) for the purpose: to restore the stump, for the reinforcement of filling material.
5) by form: conic, cylindrical, conic-cylindrical.
Every system of pins includes 4 elements: drill, pin, dentin and filling material.
Indications for use:
1. Pins as specific retentive filling material is mainly used in standard situations of IV and II classes, replacing the additional retentive cavity or deep cutting, that weaken the tooth.
2. The use of pins in large cavities, where the tooth is low tissue. This refers to the class V cavities or badly damaged bits with no humps or 3 or more surfaces.
3. Traumatic destruction of the front teeth with crowns Chip angle or just cutting edge,
4. The use of pins in pulpless teeth should be limited. All load, should take the intracanal pin - post. Use with pins to more evenly distribute the load and prevent the displacement of restoration around the post (pin) threatens root fractures, especially in the short post.
5. Splinting of the tooth crown pins for defects with preserved two walls.
6. Pins can be used to restore non-carious defects.
Pin must have the following qualities:

 1. Provide long endodontic obturation;
1. Provide long endodontic obturation;
2. Consider the anatomy of the root canal and the resistance of the tooth;
3. Provides reliable retention of coronal obturation;
4. Not corrosive residual dentin;
5. Provide restoration of crown-root part of the tooth in the simplest way;
6. Remains tight endodontic treatment by cementing of the pin;
7. To allow starting the repeated- endodontic treatment by free removing of retentive elements.
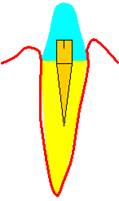
Pic. 1. Correct and incorrect statement of the pin.