Types of stratification profile
| Upper class |  
|  
| 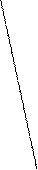 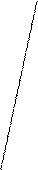
| |
| Middle class |  
| |||
| Lower class | ||||
| a) | b) | c) |
Picture 1. a) rhombus; b) pyramid with broad footing; c) pyramid with narrow footing.
The stratification profile may speak a lot of stability in the society. Its extreme stretching or increase of social distance between the poles of differentiation of the society (as in case c) leads to strengthening social tension in the society. On the other hand, extreme compression (as in case b) can also have negative consequences as egalitarian principles in income, property, power, status positions deprive people of both important stimuli to activities and source of social development, which is social inequality. In other words, it leads to stagnation of the society.
Sociologists are unanimous in their opinion that middle class plays an important role in ensuring stability in the society. Sociological surveys prove that in modern Western countries middle class accounts for about 60% of the population. Occupying an intermediate position in a social hierarchy it serves as a kind of shock-absorber that partially puts out contradictions arising between the poles of social differentiation of the society and reduces the poles’ opposition. The larger is the share of the middle class in the population the larger is the impact it has on the socio-economic policy of the state, on formation of the public opinion etc.
I Vocabulary
- stratification profile – графическое изображение стратификации
- status incompatibility – несовместимость статусов
- to go beyond – превышать
- dispersion of parameters – разброс параметров
- to testify – свидетельствовать
- to liquidate – ликвидировать
- to entail – вызывать
- frustration – разочарование
- ratio – пропорция
- stretching – напряжение
- social tension – социальное напряжение
- compression – сжатие, сдавливание
- stagnation of the society – стагнация общества, общественный застой
- unanimous – единодушный, единогласный
- transitive society – транзитивное общество
II COMPREHENSION CHECK
- What is status incompatibility?
- When does status incompatibility turn to stratification incompatibility?
- How can stratification incompatibility be liquidated?
- Why can’t it be done in a transitive society?
- What does a stratification profile show?
- What graphical forms can the stratification profile have?
- What leads to strengthening social tension in the society?
- What leads to stagnation of the society?
- What class plays an important role in ensuring stability in the society? Why?
Unit VIII