Satellite and Ground Systems of Mobile Network and Broadcasting
UNIT I
NETWORKS
Part A
Word List
| accessible | /qk'sesqbl/ | доступный, достижимый |
| appliance | /q'plaIqns/ | прибор, устройство |
| architecture | /'Q:kItektSq/ | архитектура, структура, модель |
| attach | /q'txtS/ | прикреплять, присоединять |
| box | /bPks/ | блок, модуль, стойка |
| broadband | /'brO:dbxnd/ | широкий диапазон, ширина полосы пропускания, широкополосный канал связи; широкополосный |
| circuit | /'sq:kIt/ | схема, цепь, контур |
| coax | /'kquxks/ | коаксиальный кабель, коаксиальная линия передачи |
| combine | /kPm'baIn/ | объединять, сочетать |
| configure | /kqn'fIgq/ | формировать, придавать форму; конфигурировать |
| connect | /kq'nekt/ | соединять, присоединять |
| contain | /kqn'teIn/ | содержать, вмещать |
| context | /'kPntekst/ | контекст; ситуация, окружение, среда |
| customer | /'kAstqmq/ | заказчик, потребитель |
| deliver | /dI'lIvq/ | доставлять |
| digital | /'dIdZItl/ | цифровой |
| engineering | /"endZI'nIqrIN/ | техника, разработка; технология |
| traffic engineering | /'trxfIk "endZI'nIqrIN/ | трафик, рабочая нагрузка линейной связи; обмен (данными) |
| equipment | /I'kwIpmqnt/ | оборудование, аппаратура |
| evolve | /I'vPlv/ | развивать |
| feature | /'fi:tSq/ | техническая характеристика, параметр; функция, возможность |
| functionality | /"fANkSqn'alItI/ | функциональность, выполняемые функции |
| gateway | /'geItweI/ | шлюз (сети); межсетевой интерфейс; международная АТС |
| implement | /'ImplImqnt/ | выполнять, осуществлять |
| install | /In'stO:l/ | устанавливать |
| manage | /'mxnIdZ/ | управлять; справляться |
| network | /'netwq:k/ | сеть, радиотрансляционная сеть |
| overtake | /"quvq'teIk/ | догнать, наверстать; обрушиваться; овладевать |
| range | /reIndZ/ | диапазон, интервал; класс |
| rate | /reIt/ | скорость, интенсивность, тариф |
| record | /'rekO:d/ | запись |
| roll out | /rqul aut/ | развертывать |
| router | /'ru:tq/ | маршрутизатор; программа маршрутизации |
| share | /Seq/ | разделять, совместно использовать |
| standardization | /"stxndqdaI'zeISqn/ | стандартизация, нормализация; проверка |
| storage | /'stO:rIdZ/ | хранение, накопление; запоминающее устройство, память |
| support | /sq'pO:t/ | поддерживать, содействовать |
| switch | /swItS/ | переключать, включать, выключать |
| transfer | /'trxnsfq:/ | перенос, перемещение; передача (данных); переключение (на другой источник питания) |
| wire | /'waIq/ | проволока, провод; (диэлектрический) волновод |
| wiring | /'waIqrIN/ | (электрическая) проводка, монтаж |
1. Define the following words as part of speech and give the initial words of the following derivatives.
Simplest, sharing, connection, customer, installed, managed, router, simultaneously, wireless, wiring, digital, storage.
2. Give Russian words with similar roots.
Printer, provider, server, functionality, component, modem, cable, internet, combine, separate, machines, containing, client, technology, video, professionally, player, stereo, alternative.
3. Translate the following words paying attention to the suffixes.
Controller, allowed, configured, evolves, appliance, accessible, residential, router, local, usually, entertainment, older, environment, alliance.
4. Fill in the gaps with words derived from the words in brackets.
1. Some devices that … (use) in a personal area network are printers, fax machines, telephones and scanners.
2. It is expected … (increasing) with technology improvements.
3. Personal area networks … (wire) with computer buses.
4. A home network is used … (connection) multiple devices within the home.
5. Recently telephone companies … (use) home networking.
6. This device makes it possible to connect people to the internet … (simultaneous).
7. Network controllers can be installed … (allowed) them to connect to networks.
5. Read the text and name the key points raised in it.
Home Network
A home network is a residential local area network, and is used to connect multiple devices within the home.
The simplest home networks are used to connect two or more PCs for sharing files, printers, and a single connection to the Internet (usually broadband Internet through a cable or DSL1 provider). A server can be added for increased functionality.
More recently telephone companies such as AT&T and British Telecom have been using home networking to provide triple play services (voice, video and data) to customers. These use IPTV to provide the video service. The home network usually operates over the existing home wiring (coax in North America, phone wires in multi dwelling units and powerline in Europe). These home networks are often professionally installed and managed.
Let us consider an example of a simple home network.
A home network may consist of the following components:
1. A broadband modem for connection to the internet (either a DSL modem using the phone line, or cable modem using the cable internet connection).
2. A residential gateway (sometimes called a router) connected between the broadband modem and the rest of the network. This enables multiple devices to connect to the internet simultaneously. Residential gateways, hubs/switches, DSL modems, and wireless access points are often combined.
3. A PC, or multiple PCs including laptops.
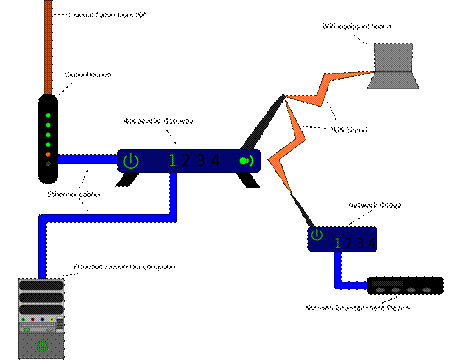
Fig 1. Network Devices
4. A wireless access point, usually implemented as a feature rather than a separate box, for connecting wireless devices.
5. Entertainment peripherals ‑ an increasing number of devices can be connected to the home network, including DVRs2, digital audio players, games machines, stereo system, and IPset-top box.
6. Internet Phones (VoIP3).
7. A network bridge connects two networks together, often giving a wired device, e.g. Xbox, access to a wireless network.
8. (Rarely) a network hub/switch ‑ a central networking hub containing a number of Ethernet ports for connecting multiple networked devices.
9. A network attached storage (NAS4) device can be used for storage on the network.
10. A print server can be used to share printers among computers on the network.
Older devices may not have the appropriate connector to the network. USB and PCI5 network controllers can be installed in some devices to allow them to connect to networks.
Network devices may also be configured from a computer. For example, broadband modems are often configured through a web client on a networked PC. As networking technology evolves, more electronic devices and home appliances are becoming Internet ready and accessible through the home network. Set-top boxes6 from cable TV providers already have USB and Ethernet ports “for future use”.
Notes:
1DSL – digital subscriber line – цифровая абонентская линия.
2DVR – digital video recorder – цифровой видеомагнитофон.
3VoIP – Voice IP – передача голоса (голосового трафика) по IP сетям, голос поверх IP, телефония на базе IP.
4NAS – network attached storage – подключаемый к сети накопитель или кластер накопителей, сетевая подсистема памяти, сетевая система хранения данных.
5PCI – peripheral components interconnect – PCI-шина, компьютерная шина со скоростью передачи данных до 33 Мб/с.
6Set-top box – телефонная абонентская приставка.
6. Read the following statements and say whether they are true or false. Correct the false ones.
1. A home network is a personal area network.
2. A server can be added for increased storage capacity.
3. Telephone companies such as AT&T and British Telecom have recently been using home networking to provide double play services to customers.
4. The home network usually operates over coax in North America, phone wires in multi dwelling units (MDU) and powerline in Europe.
5. A home network may comprise a narrowband modem.
6. A residential gateway links the broadband modem and the rest of the network.
7. A residential gateway enables multiple devices to connect to the internet one at time.
8. USB and PCI network controllers must be installed in all devices to allow them to connect to networks.
7. Match the parts to complete the sentences.
| 1. A wireless access point can be used 2. Entertainment peripherals 3. A network bridge 4. A network attached storage (NAS) device can be used 5. A print server can be used | a) to share printers among computers on the network. b) connects two networks together. c) for storage on the network. d) are an increasing number of devices that can be connected to the home network. e) for connecting wireless devices. |
8. Read paragraphs 1 and 2 and describe the essence of a home network.
9. Using information of paragraph 3, describe services that can be provided by telephone companies such as AT&T and British Telecom.
10. Make the description of a simple home network using the text and Fig.1.
11. Make an outline of the text.
12. Make a short summary of the text in written form using your outline.
Part B
13. Study the key words and word combinations of the following text. Guess the topical question of it.
Local area network (LAN), wired or wireless LAN, different IEEE protocol, to interconnect local devices, to connect the internet, the defining characteristics of LANs.
14. Read the text and find out the topical sentences of the paragraphs.
15. Find 1 or 2 sentences which can be omitted as inessential in each logical part.
16. Read the text and write out key words and phrases revealing the contents of the text.
Local Area Network
A network covering a small geographic area, like a home, office, or building. Current LANs1 are most likely to be based on Ethernet technology. For example, a library may have a wired or wireless LAN for users to interconnect local devices (e.g., printers and servers) and to connect to the internet. On a wired LAN, PCs in the library are typically connected by category 5 (Cat5) cable, running the IEEE2 802.3 protocol through a system of interconnected devices and eventually connect to the Internet. The cables to the servers are typically on Cat 5e enhanced cable, which will support IEEE 802.3 at 1 Gbit/s. A wireless LAN may exist using a different IEEE protocol, 802.11b, 802.11g or possibly 802.11n. The staff computers can get to the color printer, checkout records, and the academic network and the Internet. All user computers can get to the Internet and the card catalog. Each workgroup can get to its local printer. Note that the printers are not accessible from outside their workgroup.
This is a typical library network, in a branching tree topology and controlled access to resources (fig 2).
All interconnected devices must understand the network layer (layer 3), because they are handling multiple subnets (the different colors). Those inside the library, which have only 10/100 Mbit/s Ethernet connections to the user device and a Gigabit Ethernet connection to the central router, could be called “layer 3 switches” because they only have Ethernet interfaces and must understand IP. It would be more correct to call them access routers, where the router at the top is a distribution router that connects to the Internet and academic networks’ customer access routers.
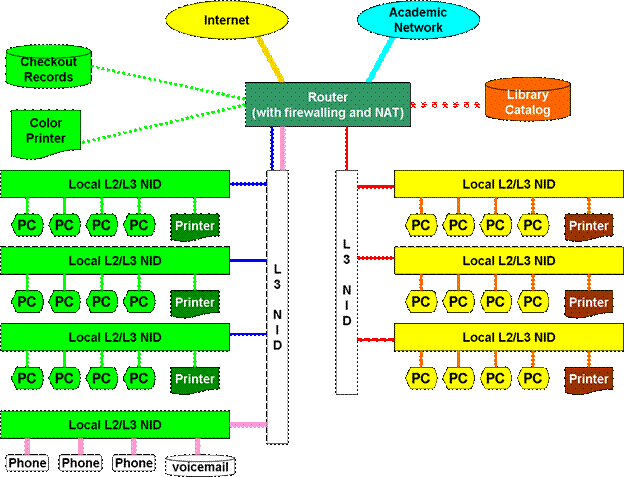
Fig 2. Library Network
The defining characteristics of LANs, in contrast to WANs (wide area networks), include their higher data transfer rates, smaller geographic range, and lack of a need for leased telecommunication lines. Current Ethernet or other IEEE 802.3 LAN technologies operate at speeds up to 10 Gbit/s. This is the data transfer rate. IEEE has projects investigating the standardization of 100 Gbit/s, and possibly 40 Gbit/s.
Notes:
1LAN – local area network – локальная сеть.
2IEEE – Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers – Институт инженеров по радиоэлектронике.
3NAT – network address translation – преобразование сетевых адресов.
4Local L2/L3NID – местная сетевая информационная база данных.
17. Sum up the text using the key words and word combinations and the topical sentences.
18. Express your attitude to the facts given in the text. You may use the following phrases:
– it is full of interesting information … ;
– I find the text rather/very cognitive …;
– I’ve learnt a lot … ;
– I don’t agree with it … .
19. Say which facts presented in the text you’ve already been familiar with.
20. Make a questionnaire to the text and interview your partner on the problems raised in the text.
Part C
21. Read the title of the text and say what information is presented in it.
22. Scan the following text and say what problem is described in the text.
Architecture and Context
The PSTN1 was the earliest example of traffic engineering to deliver Quality of Service (QoS2) guarantees. A.K. Erlang (1878 – 1929) is credited with establishing the mathematical foundations of methods required to determine the amount and configuration of equipment and the number of personnel required to deliver a specific level of service.
In the 1970s the telecommunications industry conceived that digital services would follow much the same pattern as voice services, and conceived a vision of end-to-end circuit switched services, known as the Broadband Integrated Services Digital Network (B-ISDN3). The B-ISDN vision has been overtaken by the disruptive technology of the Internet. Only the oldest parts of the telephone network still use analog technology for anything other than the last mile loop to the end user, and in recent years digital services have been increasingly rolled out to end users using services such as DSL4, ISDN5, FTTX and cable modem systems.
Many observers believe that the long term future of the PSTN is to be just one application of the Internet – however, the Internet has some way to go before this transition can be made. The QoS guarantee is one aspect that needs to be improved in the Voice over IP (VoIP) technology.
There are a number of large private telephone networks which are not linked to the PSTN, usually for military purposes. There are also private networks run by large companies which are linked to the PSTN only through limited gateways, like a large private branch exchange (PBX6).
Notes:
1PSTN – postal telephone network – почтовая телефонная сеть связи; public switched telephone network – коммутируемая телефонная сеть общего пользования.
2QoS – Quality of Service – качество обслуживания.
3B‑ISDN – the Broadband Integrated Services Digital Network – широкополосная цифровая сеть с интегрированным обслуживанием.
4DSL – Digital Subscriber Line – цифровая абонентская линия.
5ISDN – integrated-service digital network – интегральная цифровая сеть связи.
6PBX – private branch exchange – учрежденческая телефонная станция с исходящей и входящей связью.
23. Find the following information in the text.
1. Digital technology as an advanced technology in the telecommunications industry.
2. The application of the PSTN in the future.
24. Say where the information presented in the text can be used.
UNIT II
Satellite and Ground Systems of Mobile Network and Broadcasting
Part A
Word List
| access | //'xkses/// | доступ |
| affiliate | //'qfIlIeIt// | компания-филиал, партнер |
| alpha-numeric | //"xlfqnjH'merIk// | содержащий буквенные и цифровые данные |
| angle | //'xNgl// | угол |
| cache | //kxS// | прятать про запас |
| disseminate | //dI'semIneIt// | распространять |
| gear | //gIq(r)// | включаться, приводить в движение |
| handheld | //'hxndheld// | умещающийся в руке |
| latency | //'leIt(q)nsi// | скрытое состояние |
| link | //lINk// | канал связи |
| perigee | //'perIdZi:// | перигей |
| wireline | //'waIqlaIn// | телефонный кабель |
1. Compare the meanings of the following English words with the Russian ones. They may have different meaning.
Class, distribution, equator, generation, geosynchronous, globe, inadequate, location, multi-megabit, orbit, polar, present, sensor, system, terminal, unique, place, transmission.
2. Read the following words in each line and define their roots. Translate the words into Russian:
1) apply, application, applicator;
2) distribute, distribution, distributive, distributor;
3) communicate, communication, communicative, communicator;
4) transmit, transmitter, transmission;
5) generate, generation, generational, generative, generator.
3. Fill in the gaps with words derived from the words in brackets.
1. Geosynchronous systems have several advantages in terms of long satellite life and wide area … (cover) by a small number of satellites.
2. OmniTRACS provides two-way communications as well as … (locate) positioning.
3. The system is used … (extensive) for alphanumeric … (message) and on-board sensor reading for trucking fleets.
4. Newer generations of Inmarsats are incorporating … (digit) techniques for use with smaller, … (little) expensive terminals.
5. The advantages of little LEOs are their small size and … (relative) low costs.
6. The system presents considerable challenges for … (apply) development.
4. Translate the following sentences paying attention to the words in bold type. What part of speech do they belong to?
1. However, LEOs require substantially greater numbers of satellites to provide adequate coverage, and these will need more frequent replacement.
2. Qualcomm's OmniTRACS provides two-way communications as well aslocation positioning.
3. Beyond its current ability to distribute digital video, it is ripe for data communications experimentation and pilot applications development.
4. Unlikethe other mobile satellite systems, DBS is not intended to be used as a two-way system over the satellite segment.
5. The downlink data rate is between 5 Kbps and 15 Kbps while the uplink is between 55 bps and 165 bps.
6. The data communications uplink is provided through wireline networks such as the public switched telephone system (PSTN) and Internet gateways.
7. These weaknesses are addressed by the low earth orbit systems, which follow elliptical orbits, allowing them to provide reduced delays and better coverage and elevation angles when close to their orbital perigee.
5. Read the text and name the key points raised in it.
6. Divide the text into logical parts and entitle them.
7. Choose the adjectives and adverbs used to describe:
a) the advantages of geosynchronous systems;
b) the disadvantages of geosynchronous systems;
c) big LEOs’ capabilities;
d) little LEOs’ capabilities.