Basic data processing operations
ВАРИАНТЫ ДОМАШНЕЙ КОНТРОЛЬНОЙ РАБОТЫ № 3
ПО ДИСЦИПЛИНЕ «АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК»
для студентов специальностей
Программирование в компьютерных системах
Информационные системы (по отраслям)
Разработали
преподаватели дисциплины
«Английский язык»
С.В. Коваленко
Н.Н. Немкова
Красноярск, 2016
Методические рекомендации к выполнению домашней контрольной работы № 3
Варианты домашней контрольной работы предназначены для студентов заочного отделения специальностей 09.02.03. Программирование в компьютерных системах, 09.02.04 Информационные системы (по отраслям), самостоятельно изучающим дисциплину Английский язык.
Цель курса – сформировать у будущего специалиста необходимые знания предмета профессиональной деятельности, совершенствования его иноязычной речи, а также овладение иностранным языком как средством профессионального общения и предметом изучения.
В результате изучения курса студент должен
знать:
- лексический минимум по каждой теме;
- грамматические правила по темам, предусмотренными рабочей программой;
уметь:
- читать и переводить (со словарем) тексты соответствующей тематики, пересказывать их, отвечать на вопросы к тексту и выражать свое отношение к нему;
- задавать вопросы по каждой теме и отвечать на них;
иметь навык в:
- использовании в речи лексики по изученным темам;
- чтении и понимании текстов соответствующей тематики.
Изучение курса предполагает промежуточную аттестацию в виде недифференцированного зачета.
Домашняя контрольная работа содержит 15 вариантов. При самостоятельной работе над темой рекомендуется внимательно изучить грамматические правила, пользуясь списком рекомендуемой литературы. Первым заданием является изучение новых слов, которые встретятся в тексте. Слова необходимо отчитать правильно фонетически. Второе задание предполагает чтение и устный перевод текста содержащего профессионально-направленную лексику, с целью понимания основного содержания. При переводе студент может пользоваться как словарями в печатном издании, так и он-лайн словарями в интернете. Не рекомендуется загружать в переводчик полностью предложение. Оно может быть переведено некорректно.
В третьем задании предлагается ответить на вопросы к тексту. Цель: нахождение необходимой информации в тексте. Отвечать следует полным ответом на английском языке.
После перевода текста, необходимо выполнить упражнения, указанные в задании 4, 5, 6.
Пишите аккуратным, разборчивым почерком, через строчку, соблюдая поля. Можно предоставить работу в печатном варианте. Упражнения выполняйте в том же порядке, в каком они даны в домашней контрольной работе.
После получения результатов выполнения работы сделайте работу над ошибками (если у вас есть недочеты). На защите контрольной работы студент должен ориентироваться в грамматическом материале, уметь фонетически правильно читать и переводить текст (своего варианта), высказывать свое отношение к прочитанному тексту.
Вариант 1
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1, отчитайте их правильно фонетически:
data processing — обработка информации (данных)
to convert — преобразовывать; переводить (в др. единицы)
to accomplish — завершать, заканчивать; осуществлять, выполнять.
to house — помещать, размещать
to improve — улучшать, совершенствовать
to control — управлять, регулировать; управление, регулирование
to store — хранить, запоминать, заносить (размещать) в памяти
storage — запоминающее устройство, память; хранение
resource — ресурс; средство; возможность
facility — устройство; средство
facilities — приспособления; возможности
equipment — оборудование; аппаратура; приборы; устройства
available — доступный; имеющийся (в наличии); возможный
display — дисплей; устройство (визуального) отображения; показ
manner — способ, образ (действий)
sequence — последовательность, порядок (следования)
successively — последовательно
data storage hierarchy — иерархия (последовательность) запоминания информации (данных)
enter— входить; вводить (данные); заносить, записывать
comprehensive groupings — полные, обширные, универсальные образования
meaningful — имеющий смысл; значащий (о данных)
item — элемент; составная часть
record — запись, регистрация; записывать, регистрировать
file — файл; заносить (хранить) в файл
set — набор; множество; совокупность; серия; группа; система
data base — база данных
related — смежный; взаимосвязанный; относящийся (к ч.-л.)
2. Прочтите и устно переведите текст и скажите, как вы понимаете термины «обработка информации» и «иерархия запоминания информации».
Text 1. DATA PROCESSING AND DATA PROCESSING SYSTEMS
The necessary data are processed by a computer to become useful information. In fact this is the definition of data processing. Data are a collection of facts — unorganized but able to be-organized into useful information. Processing is aseries of actions or operations that convert inputs into outputs. When we speak of data processing, the input is data, and the output is useful information. So, we can define data processing as a series of actions or operations that converts data into useful information.
We use the term data processing system to include the resources that are used to accomplish the processing of data. There are four types of resources: people, materials, facilities, and equipment. People provide input to computers, operate them, and use their output. Materials, such as boxes of paper and printer ribbons, are consumed in great quantity. Facilities are required to house the computer equipment, people and materials. The need for converting facts into useful information is not phenomenon of modern life. Throughout history, and even prehistory, people have found it necessary to sort data into forms that were easier to understand. For example, the ancient Egyptians recorded the ebb and flow of the Nile River and used this information to predict yearly crop yields.*Today computers convert data about land and water into recommendations to farmers on crop planting. Mechanical aids to computation were developed and improved upon in Europe, Asia, and America throughout the seventeenth, eighteenth, and nineteenth centuries. Modern computers are marvels of an electronics technology that continues to produce smaller, cheaper, and more powerful components.
Basic data processing operations
Five basic operations are characteristic of all data processing systems: inputting, storing, processing, outputting, and controlling. They are defined as follows.
Inputting is the process of entering data, which are collected facts, into a data processing system. Storing is saving data or information so that they are available for initial or for additional processing. Processing represents performing arithmetic or logical operations on data in order to convert them into useful information. Outputting is the process of producing useful information, such as a printed report or visual display ontrolling is directing the manner and sequence in which all of the above operations are performed.
Data storage hierarchy
It is known that data, once entered, are organized and stored in successively more comprehensive groupings. Generally, these groupings are called a data storage hierarchy. The general groupings of any data storage hierarchy are as follows.
1) Characters, which are all written language symbols: letters, numbers, and special symbols. 2) Data elements, which are meaningful collections of related characters. Data elements are also called data items or fields. 3) Records, which are collections of related data elements. 4) Files, which are collections of related records. A set of related files is called a data base or a data bank.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте письменно, на английском языке на вопросы, используя информацию текста 1:
1. What is processing? 2. What is data processing? 3. What does the term of data processing system mean? 4. What basic operations does a data processing system include? 5. What is inputting / storing / outputting information? 6. What do you understand by resources? 7. How did ancient Egyptians convert facts into useful information? 8. When were mechanical aids for computation developed? 9. What does data storage hierarchy mean? 10. What are the general groupings of any data storage hierarchy?
4. Найдите в тексте и выпишите английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
Системы обработки информации; определение (термина) обработки данных; совокупность фактов; последовательность действий; преобразование входных данных в полезную информацию; включать ресурсы; завершить обработку данных; обеспечивать ввод информации в компьютер; ленты принтера; расходовать в большом количестве; размещать компьютерное оборудование; нуждаться (требовать) в приспособлениях; явление современной жизни; на протяжении доисторического периода; превращать информацию в выражения; регистрировать отливы и приливы; прогнозировать урожай зерновых культур; механические средства вычисления; ввод данных; хранение данных; первоначальная обработка данных; дополнительная обработка; выдача полезной информации; напечатанное сообщение; зрительное отображение; последовательность запоминания информации; записанные символы языка; элементы информации; база данных; набор взаимосвязанных файлов.
5. Переведите письменно, на русский язык следующие цепочки существительных:
Data resource; storage resource; network resource; security resource; system resource.
Communication facilities; data base facilities; display facilities; management facilities.
Distance control; device control; keyboard control; position control; program control.
Computer storage; laser storage; file storage; disk storage; data storage hierarchy.
Character sequence; instruction sequence; message sequence; pulse sequence.
Batch file; catalog file; data file; help file; input file; output file; menu file; user file.
Command input; data input; disk input; file input; keyboard input; program input.
6. Подберите к терминам, данным в левой колонке, определения, представленные справа, запишите полученные пары цифр-букв:
1. Computer a) the set of instructions that direct
the operations of computers;
2. Computer literacy b) a part of a computer, entering
data into the device;
3. A program c) facts unorganized but able to be
organized;
4. Data d) the output of a data processing
system;
5. Data processing e) possessing sufficient knowledge
of how computers work and what they can do to use them as problem-solving tools;
6. Data processing f) a series of operations that results
in the conversion of data system into useful information
7. Input g) an electronic device performing calculations on numerical data;
8. Output h) an electronic device accepting
the data processing results from the computer and displaying them;
9. Useful information i) a set of related files;
10. Data bank j) the resources required to accomplish the processing of data. These resources are personnel, material, facilities and equipment.
Вариант 2
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2, отчитайте их правильно фонетически:
Manual — ручной, выполняемый вручную
to take advantage of smth — воспользоваться ч.-л.
capability — способность; возможность; характеристика
accuracy — точность; правильность; четкость (изображения)
vulnerable — оставаться уязвимым, чувствительным
invalid data — неверные, неправильные, недопустимые данные
communications networks — сети передачи данных; сети связи
travel — перемещение; прохождение; путь; ход
instant response — мгновенный ответ (реакция)
to respond — отвечать; реагировать
access —доступ; обращение; обращаться, иметь доступ
capacity of storage — объем (емкость) памяти
to retrieve — извлекать, выбирать (данные); восстанавливать (файл)
value — значение; величина; значимость; ценность; оценка; оценивать
objective — цель; требование; целевая функция
cost-effective — экономичный; экономически оправданный
challenge — трудность; препятствие; представлять трудность
2. Прочтите текст, устно переведите его и скажите, каковы основные достоинства компьютеров:
Text 2. ADVANTAGES OF COMPUTER DATA PROCESSING
Computer-oriented data processing systems or just computer data processing systems are not designed to imitate manual systems. They should combine the capabilities of both humans and computers. Computer data processing systems can be designed to take advantage of four capabilities of computers.
1. Accuracy. Once data have been entered correctly into the computer component of a data processing system, the need for further manipulation by humans is eliminated, and the possibility of error is reduced. Computers, when properly programmed, are also unlikely to make computational errors. Of course, computer systems remain vulnerable to the entry by humans of invalid data.
2. Ease of communications. Data, once entered, can be transmitted wherever needed by communications networks. These may be either earth or satellite-based systems. A travel reservations system is an example of a data communications network. Reservation clerks throughout the world may make an enquiry about transportation or lodgings and receive an almost instant response. Another example is an office communications system that provides executives with access to a reservoir of date, called a corporate data base, from their personal microcomputer workstations.
3. Capacity of storage. Computers are able to store vast amounts of information, to organize it, and to retrieve it in ways that are far beyond the capabilities of humans. The amount of data that can be stored on devices such as magnetic discs is constantly increasing. All the while, the cost per character of data stored is decreasing.
4. Speed. The speed, at which computer data processing systems can respond, adds to their value. For example, the travel reservations system mentioned above would not be useful if clients had to wait more than a few seconds for a response. The response required might be a fraction of a second.
Thus, an important objective in the design of computer data processing systems is to allow computers to do what they do best and to free humans from routine, error-prone tasks. The most cost-effective computer data processing system is the one that does the job effectively and at the least cost. By using computers in a cost-effective manner, we will be better able to respond to the challenges and opportunities of our post-industrial, information-dependent society.
3. Ответьте на вопросы письменно, на английском языке, используя информацию из текста:
1. What capabilities should data-processing systems combine when designed?
2. What are the main advantages of computers?
3. What do you know of computers accuracy?
4. What is the function of communication networks?
5. Give examples of a data communication network.
6. What do you understand by capacity storage?
7. What other values of computer data processing systems do you know?
8. What is an important objective in the design of computer data processing systems?
9. What is the most effective computer data processing system?
10. What is the best way of responding to the challenges and opportunities of our post-industrial society?
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний, выпишите их:
Система обработки информации компьютером; система ориентирования на обработку данных компьютером; сочетать возможности человека и машины; ограничивать управление; вряд ли допустят ошибку; оставаться уязвимым; недопустимые данные; легкость осуществления связи; сеть передачи информации; системы, основанные на использовании спутников; служащие по резервированию жилья; получить мгновенный ответ; наводить справки; хранилище данных; корпоративная база данных; объем памяти; запоминать огромное количество информации; извлекать информацию; добавить значимости; упомянутый выше; доля секунды; подверженный ошибкам; экономически оправданный,
5. Вспомните значение новых слов и догадайтесь о значении их производных, запишите их перевод:
То eliminate: elimination; eliminable; eliminator; unlimited.
To respond: respondent; response; responsible; irresponsible; responsibility.
Accuracy: inaccuracy; accurate; inaccurate; accurately.
Correctly: correct; incorrect; to correct; correction; correctional; corrective; corrector.
Vulnerable: invulnerable; vulnerability; invulnerability.
Invalid: valid; invalidity; validity;
Access: accessible; inaccessible; accessibility; inaccessibility.
6. Преобразуйте письменно предложения, содержащие модальные глаголы, в а) прошедшее время; б) будущее время.
1. Computers can replace people in dull routine work. 2. The program is a set of instructions that may also include data to be processed. 3. Computer-controlled robots must increase the productivity of industry. 4. They can help in making different decisions. 5. The pupils may work with computers at the lessons. 6. Electric pulses can move at the speed of light. 7. Storage devices must have capacities for the input, output data and programs and for intermediate results. 8. Business minicomputers can perform to 100 million operations per second. 9. In order to solve scientific problems researchers must deal with the language of science — mathematics. 10. Programmers must write application programs in a way that computers can understand.
Вариант 3
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 3, отчитайте их правильно фонетически:
architecture - архитектура; структура
architect — разработчик архитектуры (системы, структуры)
unit — устройство; модуль; блок; элемент; составная часть
accessory equipment — вспомогательные устройства
engineering background - техническая подготовка, квалификация
analyst — аналитик; системный разработчик
product line — серия (компьютерных) продуктов
manufacturer — изготовитель; производитель; разработчик
application programmer — прикладной программист
to simulate — моделировать; имитировать
voltage — напряжение
pressure — давление, сжатие
digital computer — цифровой компьютер
hybrid computer — смешанного типа, аналого-цифровой компьютер
discrete — дискретный; отдельный
continuous quantity — непрерывная величина
on-going process —продолжающийся, постоянный, непрерывный процесс
to rely — основываться на ч.-л.;
to install — устанавливать; размещать; монтировать; настраивать
household appliances — домашние приборы / устройства
microwave oven — микроволновая печь
indoor climate control system — система регуляции температуры в доме
2. Прочтите текст, устно переведите его и скажите, о каких типах компьютеров и сферах их применения вы узнали.
Text 3.COMPUTER SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
As we know all computer systems perform the functions of inputting, storing, processing, controlling, and outputting. Now we'll get acquainted with the computer system units that perform these functions. But to begin with let's examine computer systems from the perspective of the system designer, or architect.
It should be noted that computers and their accessory equipment are designed by a computer system architect, who usually has a strong engineering background. As contrasted with the analyst, who uses a computer to solve specific problems, the computer system architect usually designs computer that can be used for many different applications in many different business. For example, the product lines of major computer manufacturers such as IBM, Digital Equipment Corporation and many others are the result of the efforts of teams of computer system architects.
Unless you are studying engineering, you don't need to become a computer system architect. However, it is important that as a potential user, applications programmer or systems analyst you understand the functions of the major units of a computer system and how they work together.
Types of computers
The two basic types of computers are analog and digital. Analog computers simulate physical systems. They operate on the basis of an analogy to the process that is being studied. For example, a voltage may be used to represent other physical quantities such as speed, temperature, or pressure. The response of an analog computer is based upon the measurement of signals that vary continuously with time. Hence, analog computers are used in applications that require continuous measurement and control.
Digital computers, as contrasted with analog computers, deal with discrete rather than continuous quantities. They count rather than measure. They use numbers instead of analogous physical quantities to simulate on-going, or real-time processes. Because they are discrete events, commercial transactions are in a natural form for digital computation. This is one reason that digital computers are so widely used in business data processing.
Machines that combine both analog and digital capabilities are called hybrid computers. Many business, scientific, and industrial computer applications rely on the combination of analog and digital devices. The use of combination analog devices will continue to increase with the growth in applications of microprocessors and microcomputers. An example of this growth is the trend toward installing control systems in household appliances such as microwave ovens and sewing machines. In the future we will have complete indoor climate control systems and robots to do our housecleaning. Analog sensors will provide inputs to the control centres of these systems, which will be small digital computers.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте письменно, на английском языке на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
1.Who designs computers and their accessory equipment? 2. What is the role of an analyst? 3. Is it necessary for a user to become a computer system architect? 4. What functions do computer systems perform? 5. What types of computers do you know? 6. What is the principle of operation of analog computers? 7. How do digital computers differ from analog computers? 8. Where are digital and analog computers used? 9. What are hybrid computers? 10. Where do they find application?
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний, выпишите их:
Функции ввода, хранения, обработки, управления ивывода информации; познакомиться; системные блоки, для начала; вспомогательные устройства; разработчик компьютерной системы; хорошая компьютерная подготовка; различные сферы применения; корпорация цифрового оборудования; прикладной программист; системный разработчик; главные устройства компьютерной системы; моделировать физические величины; измерение сигналов; в отличие от; иметь дело скорее с дискретными, чем непрерывными величинами; в режиме реального времени; коммерческие операции; цифровое вычисление; аналого-цифровые компьютеры; тенденция к установке систем управления; домашние приборы.
5. Образуйте (и переведите) имена существительные от приведенных ниже глаголов с помощью суффиксов:
A. -er, -or
То control, to compute, to design, to use, to manufacture, to work, to simulate, to operate, to protect, to process, to deal, to perform, to examine, to program, to execute, to transmit, to convert, to print, to consume, to record.
B. -tion, -sion
To organize, to collect, to combine, to apply (ic), to represent, to add, to corporate, to transact, to compute, to produce, to operate, to execute, to protect, to substitute, to prepare, to invent, to decide, to eliminate, to communicate, to correct, to inform.
С -ment
To require, to measure, to equip, to invest, to accomplish, to improve, to develop, to achieve, to displace, to govern, to move.
6. Переведите предложения, содержащие Participle I и Participle II, в функции обстоятельства:
1. When entering the Internet, I always find a lot of interesting information. 2. Though never built Babbage's analytical engine was the basis for designing today's computers. 3. When written in a symbolic language programs require the translation into the machine language. 4. While operating on the basis of analogy analog computers simulate physical systems. 5. When used voltage represents other physical quantities in analog computers. 6. Being discrete events commercial transactions are in a natural form for a digital computer. 7. As contrasted with the analyst, the computer system architect designs computers for many different applications. 8. While dealing with discrete quantities digital computers count rather than measure. 9. When using a microcomputer you are constantly making choice — to open a file, to close a file, and so on. 10. As known all computer systems perform the functions of inputting, storing, processing, controlling, and outputting.
Вариант 4
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 4, отчитайте их правильно фонетически:
hardware — аппаратное обеспечение; аппаратура; оборудование
software — программное обеспечение; программные средства
system software — системное программное обеспечение
application software — прикладное программное обеспечение
firmware — встроенное /микропроцессорное программное обеспечение
visible units — видимый блок, устройство
procedure — процедура, процесс; метод, методика; алгоритм
to associate — соединять; объединять; связывать
associated documentation — соответствующая документация
to execute applications programs — выполнять прикладные программы
payroll — платежная ведомость
inventory control — инвентаризация; переучет
investment analyses — анализ инвестиций (капиталовложений)
to protect — защищать
read-only memory (ROM) — постоянное запоминающее устройство (ПЗУ)
to refer to — относиться к; ссылаться на
to substitute — заменять; замещать
to cause — заставлять, вынуждать; причина, основание
to accomplish — завершать, заканчивать; выполнять, осуществлять
performance — производительность; быстродействие; рабочая характеристика
2. Прочтите текст, устно переведите его и объясните, как вы понимаете термины «аппаратное обеспечение» и «программное обеспечение»:
Text 4. HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, AND FIRMWARE
The units that are visible in any computer are the physical components of a data processing system, or hardware. Thus, the input, storage, processing and control devices are hardware. Not visible is the software — the set of computer programs, procedures, and associated documentation that make possible the effective operation of the computer system. Software programs are of two types: systems software and applications software.
Systems software are the programs designed to control the operation of a computer system. They do not solve specific problems. They are written to assist people in the use of the computer system by performing tasks, such as controlling all of the operations required, to move data into and out of a computer and all of the steps in executing an application program. The person who prepares systems software is referred to as a systems programmer. Systems programmers are highly trained specialists and important members of the architectural team.
Applications software are the programs written to solve specific problems (applications), such as payroll, inventory control, and investment analysis. The word program usually refers to an application program, and the word programmer is usually a person who prepares applications software.
Often programs, particularly systems software, are stored in an area of memory not used for applications software. These protected programs are stored in an area of memory called readonly memory (ROM), which can be read from but not written on. Firmware is a term that is commonly used to describe certain programs that are stored in ROM. Firmware often refers to a sequence of instructions (software) that is substituted for hardware. For example, in an instance where cost is more important than performance, the computer system architect might decide not to use special electronic circuits (hardware) to multiply two numbers, but instead write instructions (software) to cause the machine to accomplish the same function by repeated use of circuits already designed to perform addition.
3. Ответьте письменно, на английском языке на вопросы, используя информацию текста:
1.What is hardware?
2.Give the definition of software.
3. What are the types of software?
4. What are systems software?
5. What kind of tasks do systems software perform?
6. Who prepares systems software?
7. What are applications software?
8. What problems do applications software solve?
9. What is firmware?
10. How can a computer system architect use firmware?
4.Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний, выпишите их:
Видимые устройства; система обработки данных; аппаратное обеспечение; набор компьютерных программ; соответствующая документация; эффективная работа; системное программное обеспечение; прикладное программное обеспечение; системный программист; платежная ведомость; переучет; анализ инвестиций; прикладная программа; работающий только в режиме чтения; постоянное запоминающее устройство; последовательность команд; в случае; производительность; электронная цепь; умножать числа; заставить машину выполнять ту же функцию; выполнять сложение.
5. Вспомните значение новых слов переведите словосочетания, употребляемые с этими словами:
Architecture: communication architecture; computer architecture; disk architecture; microprocessor architecture; network architecture; security architecture; system architecture; virtual architecture.
Software: system software; application software; database software; disk software; educational software; game software; management software; simulation software hard ware: computer hardware; device hardware; display hardware; memory hardware; mouse hardware; network hardware; system hardware; video hardware.
Procedure: accounting procedure; computational procedure; control procedure; data-processing procedure; decision procedure; error-correcting procedure; formatting procedure; installation procedure; management procedure; solution procedure.
Protection: computer protection; data protection; device protection; display protection; error protection; hardware protection; software protection; resource protection; security protection; system protection; virus protection.
6. Озаглавьте каждый компонент текста и составьте письменно, на английском языкенебольшой пересказ к нему.
Вариант 5
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 5, отчитайте их правильно фонетически:
Operation — операция; работа; действие; срабатывание
to relate — связывать; устанавливать отношения
a broad view — широкий взгляд, обзор
unit — устройство; модуль, блок; узел; элемент; ячейка
input — ввод; устройство ввода; вводить; подавать на вход
to insert — вставлять; вносить; включать
storage memory — память; запоминающее устройство
available — доступный; имеющийся в наличии
at the appropriate time — в нужное время
arithmetic-logical unit — арифметико-логическое устройство
output — вывод; устройство вывода; выводить; подавать на выход
to remove — удалять; устранять; вынимать; исключать
control unit — блок управления
cause — заставлять; вынуждать; быть причиной; причина; основание
to feed (fed, fed) — подавать; питать; вводить (данные)
to interpret — интерпретировать; истолковывать
to issue commands — выдавать команды
pulse — no-pulse — (есть) импульс — холостой импульс
2. Прочтите текст, устно переведите его и назовите основные функциональные блоки компьютера и их назначение:
Text 5.FUNCTIONAL UNITS OF DIGITAL COMPUTERS
As we know, all computer operations can be grouped into five functional categories. The method in which these five functional categories are related to one another represents the functional organization of a digital computer. By studying the functional organization, a broad view of the computer is received.
The five major functional units of a digital computer are:
1) Input— to insert outside information into the machine;
2) Storage or memory — to store information and make it available at the appropriate time; 3) Arithmetic-logical unit — to perform the calculations; 4) Output — to remove data from the machine to the outside world and 5) Control unit — to cause all parts of a computer to act as a team.
A complete set of instructions and data are usually fed through the input equipment to the memory where they are stored. Each instruction is then fed to the control unit. The control unit interprets the instructions and issues commands to the other functional units to cause operations to be performed on the data. Arithmetic operations are performed in the arithmetic-logical unit, and the results are then fed back to the memory. Information may be fed from either the arithmetic unit or the memory through the output equipment to the outside world. The five units of the computer must communicate with each other. They can do this by means of a machine language which uses a code composed of combinations of electric pulses. These pulse combinations are usually represented by zeros and ones, where the one may be a pulse and the zero — a no-pulse. Numbers are communicated between one unit and another by means of these one-zero or pulse — no-pulse combinations. The input has the additional job of converting the information fed in by the operator into machine language. In other words, it translates from our language into the pulse — no-pulse combinations understandable to the computer. The output's additional job is converting the pulse — no-pulse combinations into a form understandable to us, such as a printed report.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Дайте письменные ответы на вопросы, на английском языке, используя информацию текста:
1. What represents the functional organization of a computer?
2. What can we get by studying the functional organization?
3. What is the function of the input device?
4. What does memory serve for?
5. What is the task of the arithmetic-logical unit?
6. What is the function of the output?
7. What is the main purpose of the control unit?
8. How do all units of the computer communicate with each other?
9. What is the additional job of the input?
10. What is the additional function of the output?
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний, выпишите их:
Функциональная организация; действия компьютера; связывать друг с другом; вводить информацию извне; делать информацию доступной; выполнять вычисления; выводить информацию; блок управления; выдавать команды; заставлять выполнять команды; выходное устройство; внешний мир; связываться друг с другом; комбинация электрических импульсов; холостой импульс; импульсы, распознаваемые компьютером.
5. Разделите приведенные ниже слова на три группы, определяя по суффиксу часть речи — существительное, прилагательное или наречие. Переведите слова:
Organization, functional, available, equipment, processor, completely, architectural, converter, convertible, controller, removable, logical, addition, additional, usually, accomplishment, operator, operation, mainly, communication, insertion, electronic, digital, instruction, generally, arithmetic, daily", development, central, lately, visible, substitution, understandable.
6. Вспомните значение новых слов и переведите словосочетания, употребляемые с этими словами:
Computer: analog computer; digital computer; hybrid computer; all-purpose computer; general-purpose computer; fifth-generation computer; game computer; handheld computer; mobile computer; multimedia computer; notebook computer; pocket computer; portable computer.
Unit: unit of memory; unit of data; unit of measurement; arithmetic unit; arithmetic-logical unit; central processing unit; computing unit; control unit; functional unit; input unit; output unit; network unit; system unit.
Function: arithmetic function; checking function; complex function; computer function; continuous function; conversion function; distribution function; encoding function; logical function; numeric function; output function; program function; search function; software function; support function; utility function; variable function.
Control: access control; batch control; coding control; distance / remote control; error control; execution control; hardware control; input/output control; memory control; power control; production control; program control; rate control; self-acting control; software control; system control.
Вариант 6
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 6, отчитайте их правильно фонетически:
large-scale — большой; крупномасштабный
flip-flop — триггер
circuit — цепь; контур; схема
employ — использовать; употреблять; применять
logic gates — логический элемент; схема пропускания (сигналов); проход
feasible — возможный; выполнимый; осуществимый
interpret orders — интерпретировать, истолковывать команды
operate switches — приводить в действие переключатели
convey — передавать; сообщать
in response to — в ответ на
correct operand — нужный операнд
original input data — исходная вводимая информация
proceed — продолжать(ся); возобновлять(ся); действовать
room — (свободное) место; свободная память
2. Прочтите текст 6, устно переведите его и скажите, какую дополнительную информацию вы узнали о действии основных устройств компьютера:
Text 6. SOME FEATURES OF A DIGITAL COMPUTER
It should be noticed that even in a large-scale digital system, such as in a computer, or in a data-processing, control or digital-communication system, there are only a few basic operations which must be performed. These operations may be operated many times. The four circuits most commonly employed in such systems are known as the OR, AND, NOT and FLIP-FLOP.They are called logic gates or circuits.
An electronic digital computer is a system which processes and stores very large amount of data and which solves scientific problems of numerical computations of such complexity and with such speed that solution by human calculation is not feasible. So the computer as a system can perform numerical computations and follow instructions with extreme speed but it cannot program itself.
You know that the numbers and the instructions which form the program, the computer is to follow, are stored in an essential part of the computer called the memory. The second important unit of the computer is the control whose function is to interpret orders. The control must convert the command into an appropriate set of voltages to operate switches and carry out the instructions conveyed by the order. The third basic element of a computer is the arithmetic device, which contains the circuits performing the arithmetic computations: addition, subtraction, etc. The control and arithmetic components are called the central processor. Finally a computer requires appropriate input-output devices for inserting numbers and orders into the memory and for reading the final result.
Suppose a command to perform an addition or division has been transmitted to the central processor. In response to this order the control must select the correct operands from the memory, transmit them to the arithmetic unit and return to the memory the result of the computation. The memory serves for storing not only the original input data, but also the partial results which will have to be used again as the computation proceeds.
Lastly, if the computation doesn't stop with the execution of this instruction and the storage of the partial result, the control unit must automatically pass on to the next instruction. The connection of the control unit back to the input permits insertion of more data when there is room in the memory.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте письменно, на английском языке на вопросы, используя информацию текста:
1. What are the most commonly used circuits in any computer?
2. How are they called?
3. What kind of a system is a digital computer?
4. Is there anything that a computer cannot do itself? What is it?
5. Where are the instructions and digits stored?
6. What is the function of the control?
7. What does the arithmetic device serve for?
8. What components form the central processor?
9. What other devices in addition to the above-mentioned ones does a computer require?
10. How are computations performed in a computer?
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих сочетаний, выпишите их:
Крупномасштабная цифровая система; система обработки данных; система цифровой связи; наиболее широко распространенные схемы; логические схемы; решать научные проблемы; выполнять числовые вычисления; интерпретировать команды; приводить в действие переключатели; выполнять команды; нуждаться (требовать) в необходимом устройстве ввода-вывода; введение чисел и команд; считывание конечных результатов; передавать команду в центральный процессор; в ответ на; хранение частичных результатов; позволить введение новых данных; свободное место в памяти.
5. Подберите пары или группы близких по значению слов из предложенных ниже. Переведите слова на русский язык:
Verbs: relate, employ, insert, perform, remove, operate, show, interpret, select, issue, use, receive, perform, cause, print, make, compute, connect, execute, take away, require, act, convert, carry out, demand, permit, demonstrate, choose, transmit, type, store, get, calculate, proceed, continue, keep, allow.
Nouns:response, unit, component, computation, storage, gate, amount, digit, element, memory, instruction, device, equipment, connection, circuit, order, command, information, relation, quantity, answer, calculation, number, data.
Adjectives:broad, complete, each, appropriate, every, basic, essential, digital, original, full, wide, initial, major, large, numerical, common, necessary, usual, important, general, great.
6. Cогласуйте слова в левой колонке с их интерпретацией, предложенной справа:
1. Functional organization of a computer a) processes and stores large amount of data and solves
problems of numerical computations;
2. Input b) circuits used in large-scale digital systems;
3. Memory c) method of interrelation of the main units of a computer
4. Control unit d) removing data from the de-vice to the outside world;
5. Output e) inserting information into the computer;
6. Arithmetic unit f) a code of combinations of electric pulses;
7. Machine language g) performs addition, subtration, multiplication, etc;
8. Logic gates h) stores original data as well as partial results;
9. Digital computer i) causes all parts of the computer to act as a team.
Вариант 7
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 7:
primary / secondary storage — первичное / вторичное запоминающее устройство
main storage — основная память; оперативное запоминающее устройство
internal storage — внутреннее ЗУ
sequence — последовательность; порядок следования
intermediate results — промежуточные результаты
ongoing process — продолжающиеся), постоянный процесс
similarity — сходство; подобие
to retain — сохранять; удерживать
to locate — размещать(ся); располагать(ся)
value — значение, величина; значимость, ценность; оценка
binary digit — двоичная цифра; двоичный знак
adjacent— смежный; соседний; примыкающий
strings of characters — последовательность символов
consecutive— последовательный; смежный; соседний
2. Прочтите текст и скажите, что такое запоминающее устройство в компьютере и о каких его типах вы узнали из текста:
Text 7.STORAGE UNITS
Computer system architecture is organized around the primary storage unit because all data and instructions used by the computer system must pass through primary storage. Our discussion of computer system units will begin with the functions of the primary and secondary storage units. This leads to the examination of the central processing unit and from there to the consideration of the input and output units. Therefore, the sequence in which we'll describe the functional units of a digital computer is: 1) storage units, primary and secondary; 2) central processing unit; 3) input and output units.
As you know, there are primary and secondary storage units. Both contain data and the instructions for processing the data. Data as well as instructions must flow into and out of primary storage.
Primary storage is also called main storage or internal storage. The specific functions of internal storage are to hold (store): 1) all data to be processed; 2) intermediate results of processing; 3) final results of processing; 4) all the instructions required for ongoing process. Another name for primary storage is memory, because of its similarity to a function of the human brain. However, computer storage differs from human memory in important respects. Computer memory must be able to retain very large numbers of symbol combinations, without forgetting or changing any details. It must be able to locate all its contents quickly upon demand. The combinations of characters, that is, the letters, numbers, and special symbols by which we usually comunicate, are coded. The codes used by computer designers are based upon a number system that has only two possible values, 0 and 1 .'A number system with only two digits, 0 and I, is called a binary number system. Each binary digit is called a bit, from Binary digit. As the information capacity of a single bit is limited to 2 alternatives, codes used by computer designers are based upon combinations of bits. These combinations are called binary codes. The most common binary codes are 8-bit codes because an 8-bit code provides for 2/8, or 256 unique combinations of l's and O's, and this is more than adequate to represent all of the characters by which we communicate.
Data in the form of coded characters are stored in adjacent storage locations in main memory in two principal ways : 1) as "strings" of characters — in bytes; and 2) within fixed-size "boxes" — in words. A fixed number of consecutive bits that represent a character is called a byte. The most common byte size is 8-bit byte. Words are usually 1 or more bytes in length.
Secondary storage. Primary storage is expensive because each bit is represented by a high-speed device, such as a semiconductor. A million bytes (that is, 8 million bits) is a large amount of primary storage. Often it is necessary to store many millions, sometimes billions, of bytes of data. Therefore slower, less expensive storage units are available for computer systems. These units are called secondary storage. Data are stored in them in the same binary codes as in main storage and are made available to main storage as needed.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста:
1. What are the functional units of a digital computer?
2. What units make up the central processing unit?
3. How is computer system organized?
4. What are the two main types of storage units?
5. What do they contain?
6. What is the function of a primary storage?
7. Why is primary storage often called memory?
8. In what respect does computer memory differ from human memory?
9. What are codes based on?
10. What is Secondary storage and what is it used for?
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих cловосочетаний:
Функциональный блок; цифровой компьютер; устройство ввода; устройство управления; арифметико-логическое устройство; центральный процессор; структура компьютерной системы; первичное запоминающее устройство; вторичное ЗУ; рассмотрение; поэтому последовательность; оперативное ЗУ; внутренняя память; промежуточные результаты; подобие функции человеческого мозга; размешать содержимое по требованию; система счисления; двоичная система счисления; возможные величины; объем информации; двоичный код; смежные ячейки памяти; последовательность символов; быстродействующее устройство; полупроводник; доступный.
5. Вспомните значение новых слов и попытайтесь перевести словосочетания, употребляемые с этими словами:
Storage: available storage; buffer storage; computer storage; data storage; magnetic disk storage; magnetic tape storage; input storage; intermediate storage; internal storage; laser storage; main storage; primary storage; secondary storage; sequential-access storage; variable storage; virtual storage.
Value: absolute value; acceptable value; additional value; binary value; byte value; character value; constant value; correct value; data value; digit value; discrete values; invalid value; negative value; numerical value; output value; valid value.
Digit: binary digit; binary-coded digit; check digit; information digit; input digit; nonsignificant digit; significant digit; digit-by-digit.
Sequence: out of sequence; alphabetic sequence; arithmetic sequence; binary sequence; character sequence; code sequence; instruction sequence; data sequence; digital sequence; historical sequence; increasing sequence; program sequence; string sequence.
6. Найдите в тексте слова, близкие по значению следующим:
Memory; element; information; command; examination; character; quantity; number; place; computer architect; likeness.
To apply; to form; to move; to hold; to demand; to connect; to supply; to place; to name; to start; to examine.
Continuous; significant; consecutive; usual; enough; main; initial; general
Вариант 8
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 8:
medium (pi. media) — носитель; среда
capacity — емкость; объем (памяти); пропускная способность
media capacity — емкость носителя
data access time — время доступа к данным
per bit — на единицу информации
to transfer— передавать(ся); переносить(ся); пересылать(ся)
archival storage — архивное ЗУ; архивная память
to depend — зависеть от; полагаться, рассчитывать на
to rotate — вращать(ся); чередовать(ся); сменять(ся)
reason — причина; основание; довод; обосновывать; делать вывод
solid-state device — твердотельный прибор
magnetic core — магнитный сердечник
bipolar semiconductor — биполярный полупроводник
metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) — структура металл-оксид-полупроводник
randomly — произвольно
random-access memory (RAM) — оперативное запоминающее устройство (ОЗУ)
sound recording — звукозапись
to arrange — размещать; располагать; устанавливать;
монтировать tape device — ЗУ на магнитной ленте
to range — классифицировать; располагать в порядке; лежать в диапазоне
magnetic disc storage — ЗУ на магнитном диске
moving-head device — устройство с двигающейся головкой
predominant — преобладающий; доминирующий
flexible —гибкий; настраиваемый; изменяемый
floppy (disk) — гибкий диск(ета); ЗУ на гибком диске
to meet the demands — удовлетворять потребности
2. Прочтите текст 8 и скажите, как вы понимаете термин «запоминающая среда» и какие компоненты ее составляют:
Text 8. STORAGE DEVICES
Storage media are classified as primary storage or secondary storage on the basis of combinations of cost, capacity, and access time. The cost of storage devices is expressed as the cost per bit of data stored. The most common units of cost are cents, millicents (0.001 cents) and microcents (0.000001 cents). The time required for the computer to locate and transfer data to and from a storage medium is called the access time for that medium. Capacities range from a few hundred bytes of primary storage for very small computers to many billions of bytes of archival storage for very large computer systems.
Memories may be classified as electronic or electromechanical. Electronic memories have no moving mechanical parts, and data can be transferred into and out of them at very high speeds. Electromechanical memories depend upon moving mechanical parts for their operation, such as mechanisms for rotating magnetic tapes and disks. Their data access time is longer than is that of electronic memories; however they cost less per bit stored and have larger capacities for data storage. For these reasons most computer systems use electronic memory for primary storage and electromechanical memory for secondary storage.
Primary storage has the least capacity and is the most expensive; however, it has the fastest access time. The principal primary storage circuit elements are solid-state devices: magnetic cores and semiconductors. For many years magnetic cores were the principal elements used in digital computers for primary storage. The two principal types of semiconductors used for memory are bipolar and metal-oxide semiconductors (MOS). The former is faster, the latter is more commonly used at present. Because data can be accessed randomly, semiconductor memories are referred to as random-access memory, or RAM.
There is a wide range of secondary storage devices. Typical hardware devices are rotating electromechanical devices. Magnetic tapes, disks, and drums are the secondary storage hardware most often used in computer systems for sequential processing. Magnetic tape, which was invented by the Germans during World War II for sound recording, is the oldest secondary storage medium in common use. Data are recorded in the form of small magnetized "dots" that can be arranged to represent coded patterns of bits.
Tape devices range from large-capacity, high-data-rate units used with large data processing systems to cassettes and cartridges used with small systems. Magnetic disk storage, introduced in the early 1960s, has replaced magnetic tape as the main method of secondary storage. As contrasted with magnetic tapes, magnetic discs can perform both sequential and random processing. They are classified as moving-head, fixed-head, or combination moving-head and fixed-head devices. Magnetic discs are the predominant secondary storage media. They include flexible, or floppy discs, called diskettes. The "floppies" were introduced by IBM in 1972 and are still a popular storage medium to meet the demands of the microcomputer market.
3. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста:
1. How are storage media classified?
2. How is the cost of storage devices expressed?
3. What is the access time for storage media?
4. How does the storage capacity range?
5. What are the two main types of storage devices?
6. What are electronic storage devices?
7. What are the principal primary storage circuit elements?
8. What are the main secondary storage devices?
9. What is the oldest secondary medium and when was it invented?
10. What is a floppy?
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
Запоминающие устройства; носители памяти; первичные ЗУ; вторичные ЗУ; время доступа; стоимость ЗУ; диапазон емкости памяти; архивная память; движущиеся механические части; вращающиеся магнитные ленты и диски; по этим причинам; твердотельные устройства; магнитные сердечники; полупроводники; оперативное ЗУ; аппаратное обеспечение вторичной памяти; звукозапись; . намагниченные точки; представлять зашифрованную комбинацию единиц информации; в отличие от магнитных лент; последовательная и произвольная обработка; устройства с движущейся и фиксированной головкой; удовлетворять потребности; гибкий диск.
5. Опишите схему:
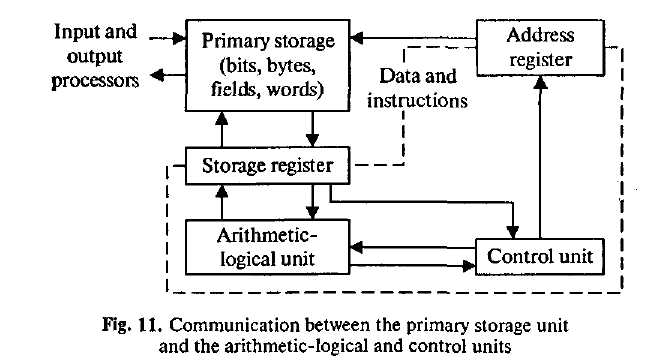
|
6. Переведите предложения, содержащие все возможные формы причастий: Participle I, Participle II, Perfect Participle Active и Perfect Participle Passive:
1.Electromechanical memories depend upon moving mechanical parts for their operation. 2. The time required for the computer to locate and transfer data to and from a storage medium is called the access time. 3. Being not visible software makes possible the effective operation of computer system. 4. Having invented magnetic tapes the Germans used them as the secondary storage medium. 5. When properly programmed computers don't make computational errors. 6. Having been introduced in the early 1960s magnetic disc storage has replaced magnetic tape storage. 7. The control unit interpreting instructions is one of the important parts of any computer system. 8. Data recorded in the form of magnetized dots can be arranged to represent coded patterns of bits. 9. As contrasted with magnetic tapes magnetic discs can perform both sequential and random processing. 10. While having no moving mechanical parts electronic memories can transfer data at very high speed.
Вариант 9
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 9:
central processing unit (CPU) - центральный процессор (ЦП)
interchangeably – взаимозаменяемым образом
precisely — точно
internal memory - внутренняя память; внутреннее ЗУ
activity - деятельность; работа; действия операции
to issue - посылать (сигнал); выводить, выдавать
(сообщение) response - ответ; отклик; реакция; отвечать; реагировать
to interprete - интерпретировать; истолковывать;
according - согласно; в соответствии с
level - уровень; степень; мера; выравнивать
input-output port - порт ввода-вывода
control unit (CU) - устройство управления
arithmetic-logical unit (ALU) - арифметико-логическое устройство
switch - переключатель; коммутатор; переключать; переходить
to direct - направлять; адресовать; указывать;
прямой; непосредственный
step-by-step operations - пошаговые операции
to select - выбирать; выделять (на экране)
on the other hand - с другой стороны
exponentiation – возведение в степень
call for — требовать; предусматривать
to load — загружать; выполнять загрузку
2. Прочтите текст 9 и скажите, какой компонент составляет сердце компьютерной системы и в чем заключается его функция:
Text 9. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
It is well known in computer science that the words 'computer' and 'processor' are used interchangeably. Speaking more precisely, 'computer* refers to the central processing unit (CPU) together with an internal memory. The internal memory, control and processing components make up the heart of the computer system. Manufactures design the CPU to control and carry out basic instructions for their particular computer.
The CPU coordinates all the activities of the various components of the computer. It determines which operations should be carried out and in what order. The CPU controls the operation of the entire system by issuing commands to other parts of the system and by acting on responses. When required it reads information from the memory, interprets instructions, performs operations on the data according to the instructions, writes the results back into the memory and moves information between memory levels or through the input-output ports.
In digital computers the CPU can be divided into two functional units called the control unit (CU) and the arithmetic-logical unit (ALU). These two units are made up of electronic circuits with millions of switches that can be in one of two states, either on or off.