Airplane Parts and Functions
Airplanes are transportation devices which are designed to move people and cargo from one place to another. Airplanes come in many different shapes and sizes depending on the mission of the aircraft. The airplane shown in the figure is a turbine-powered airliner which has been chosen as a representative aircraft.
For any airplane to fly, one must lift the weight of the airplane itself, the fuel, the passengers, and the cargo. The wings generate most of the lift to hold the plane in the air. To generate lift, the airplane must be pushed through the air. The air resists the motion in the form of aerodynamic drag. Modern airliners use winglets on the tips of the wings to reduce drag. The turbine engines, which are located beneath the wings, provide the thrust to overcome drag and push the airplane forward through the air. Smaller, low-speed airplanes use propellers for the propulsion system instead of turbine engines.
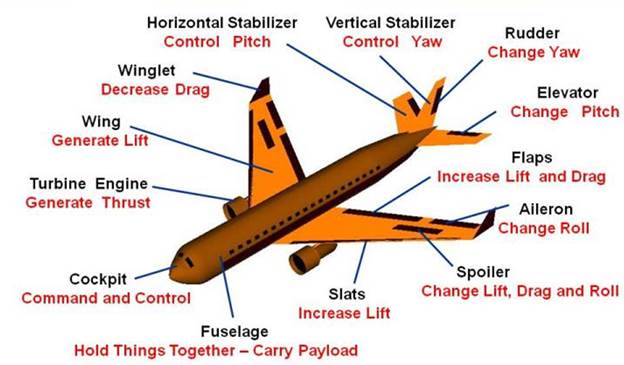 To control and maneuver the aircraft, smaller wings are located at the tail of the plane. The tail usually has a fixed horizontal piece, called the horizontal stabilizer, and a fixed vertical piece, called the vertical stabilizer. The stabilizers' job is to provide stability for the aircraft, to keep it flying straight. The vertical stabilizer keeps the nose of the plane from swinging from side to side, which is called yaw. The horizontal stabilizer prevents an up-and-down motion of the nose, which is called pitch. (On the Wright brothers’ first aircraft, the horizontal stabilizer was placed in front of the wings. Such a configuration is called a canard after the French word for "duck").
To control and maneuver the aircraft, smaller wings are located at the tail of the plane. The tail usually has a fixed horizontal piece, called the horizontal stabilizer, and a fixed vertical piece, called the vertical stabilizer. The stabilizers' job is to provide stability for the aircraft, to keep it flying straight. The vertical stabilizer keeps the nose of the plane from swinging from side to side, which is called yaw. The horizontal stabilizer prevents an up-and-down motion of the nose, which is called pitch. (On the Wright brothers’ first aircraft, the horizontal stabilizer was placed in front of the wings. Such a configuration is called a canard after the French word for "duck").
The ability to change forces gives us a means of controlling and maneuvering the airplane. The hinged part of the vertical stabilizer is called the rudder; it is used to deflect the tail to the left and right as viewed from the front of the fuselage. The hinged part of the horizontal stabilizer is called the elevator; it is used to deflect the tail up and down. The outboard hinged part of the wing is called the aileron; it is used to roll the wings from side to side. Most airliners can also be rolled from side to side by using the spoilers. Spoilers are small plates that are used to disrupt the flow over the wing and to change the amount of force by decreasing the lift when the spoiler is deployed.
The wings have additional hinged, rear sections near the body that are called flaps. Flaps are deployed downward on takeoff and landing to increase the amount of force produced by the wing. On some aircraft, the front part of the wing will also deflect. Slats are used at takeoff and landing to produce additional force. The spoilers are also used during landing to slow the plane down and to counteract the flaps when the aircraft is on the ground.
The fuselage, or body of the airplane, holds all the pieces together. The pilots sit in the cockpit at the front of the fuselage. On some aircraft, fuel tanks are in the fuselage; others carry the fuel in the wings.
Many modern aircraft feature retractable landing gear, which pull up into fuselage during flight, but others still feature fixed landing gear that remain extended all the time.
 Упражнение 1
Упражнение 1
Переведите на русский:
Lift, drag, thrust, propulsion system, winglet, vertical stabilizer, horizontal stabilizer, yaw, pitch, roll, hinges, rudder, to control, elevator, aileron, spoilers, flaps, slats, fuselage, cockpit, takeoff, landing, fuel tanks, retractable landing gear.
Упражнение 2
Ответьте на вопросы:
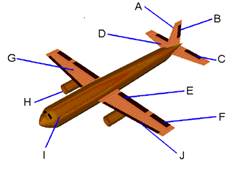
1) What are the names of the parts of the airplane pictured above?
2) What are the functions of the parts of the airplane pictured above?
3) Which parts are used to control lift at low speed for takeoff and landing?
4) Which parts, installed one to each wing, operate in opposite directions (i.e., one up and one down)?
5) If the part in Problem 4 on the right wing is up and the one on the left wing is down, what will the airplane do?
6) If the pilot lowers the elevator, what will the airplane's tail do?
7) What will this in turn cause the airplane's nose to do?
8) If the pilot moves the rudder to the left, what will the airplane's tail do?
9) What will this in turn cause the airplane's nose to do?
10) What motion will occur in an airplane with the elevator deflected up and the rudder deflected to the right?
11) What is a spoiler?